Research
Metallic nanoparticles for multimodal cancer therapy
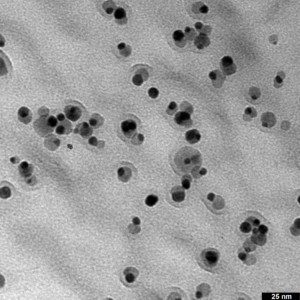
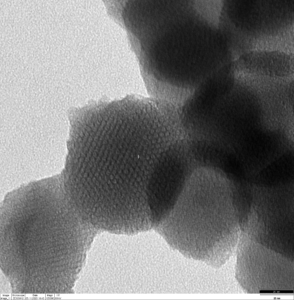
1. Synthesis and characterization of
- silicon quantum dots
- iron-doped silicon NPs
- magnetic mesoporous silica NPs
- ferrite NPs
- noble metal – Fe3O4 nanoheterodimers
2. Multimodal cancer therapy
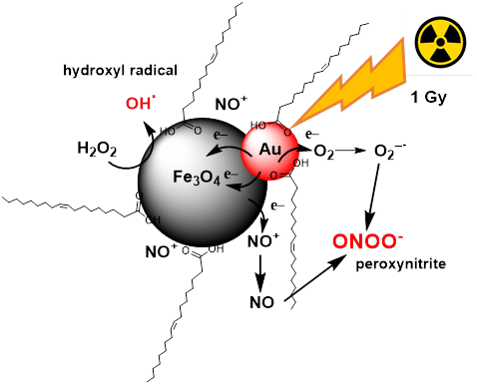
These synthesized NPs act as X-ray dose enhancers in radio-therapy by increasing the reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.
The heterogenity of tumor tissues and the resistance of cancer cells towards monotherapies indicate the necessity to combine two or more forms of cancer treatment.
For example: Combination of radio-therapy with
- chemo-therapy,
- gene-therapy,
- hypoxia treatment
whereat these nanoparticles were additionally used for the delivery of
- anticancer drugs,
- inhibitors,
- NO donors,
- siRNA.
3. Applications
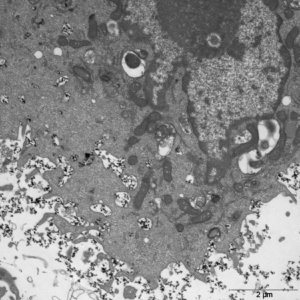
3.1 2D cell cultures
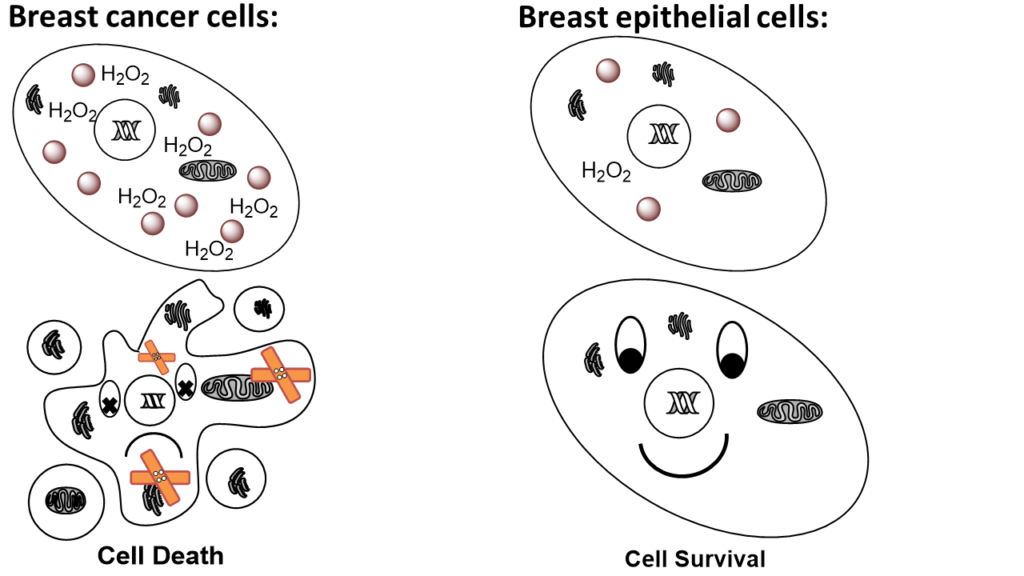
The influence of NPs on cellular and molecular level is examined via 2D cell culture studies e. g. on breast, lung and colon cancer cell lines and non-tumorogenic breast or umbilical endothelial cells.
For example studies on
- biocompatibility
- cellular uptake
- ROS production
- activity of ROS detoxifying enzymes
- cell death
3.2 3D tumor spheroids
3D cell culture are excellent models for metastases by mimicking
- 3D cellular interactions
- an extracellular matrix
- diffusion limits of oxygen and nutrients
- pH, metabolic and proliferative gradients
|
Treatment: Caffeic acid Au-Fe3O4 nanoheterodimers, X-rays (5 doses of 2 Gy) |
||
|
Tumor spheroid |
Healthy spheroid |
|
| Day 1 | 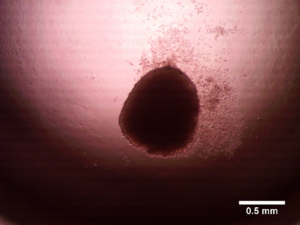 |
 |
| Day 7 | 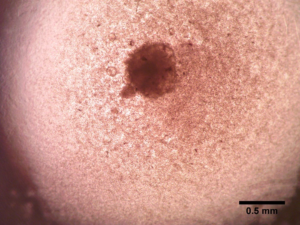 |
 |